Partial vs Total Knee Replacement: Which One Is Right for You?

Knee pain can quietly change the way you live. Activities that once felt effortless—walking, climbing stairs, sitting cross-legged, or standing for long periods—can become painful and exhausting. For many people, knee pain starts as a mild inconvenience but gradually progresses into a serious condition that limits independence and quality of life.
When medications, physiotherapy, and lifestyle changes no longer provide relief, doctors may recommend knee replacement surgery. At this point, many patients face an important question:
Should I undergo partial knee replacement or total knee replacement?
The answer depends on several medical and lifestyle factors. Understanding the difference between these two procedures can help you make an informed decision and feel confident about your treatment plan.
This article explains partial vs total knee replacement in simple, patient-friendly language, helping you understand which option may be right for you.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure in which damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial components to reduce pain and improve movement.
The knee joint is made up of three compartments:
-
Medial compartment (inner side of the knee)
-
Lateral compartment (outer side of the knee)
-
Patellofemoral compartment (front of the knee, behind the kneecap)
Arthritis or injury may affect one compartment or multiple compartments. The extent of damage plays a crucial role in deciding whether a partial or total knee replacement is required.
What Is Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement, also called unicompartmental knee replacement, is a surgical procedure in which only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced. The healthy bone, cartilage, and ligaments are preserved.
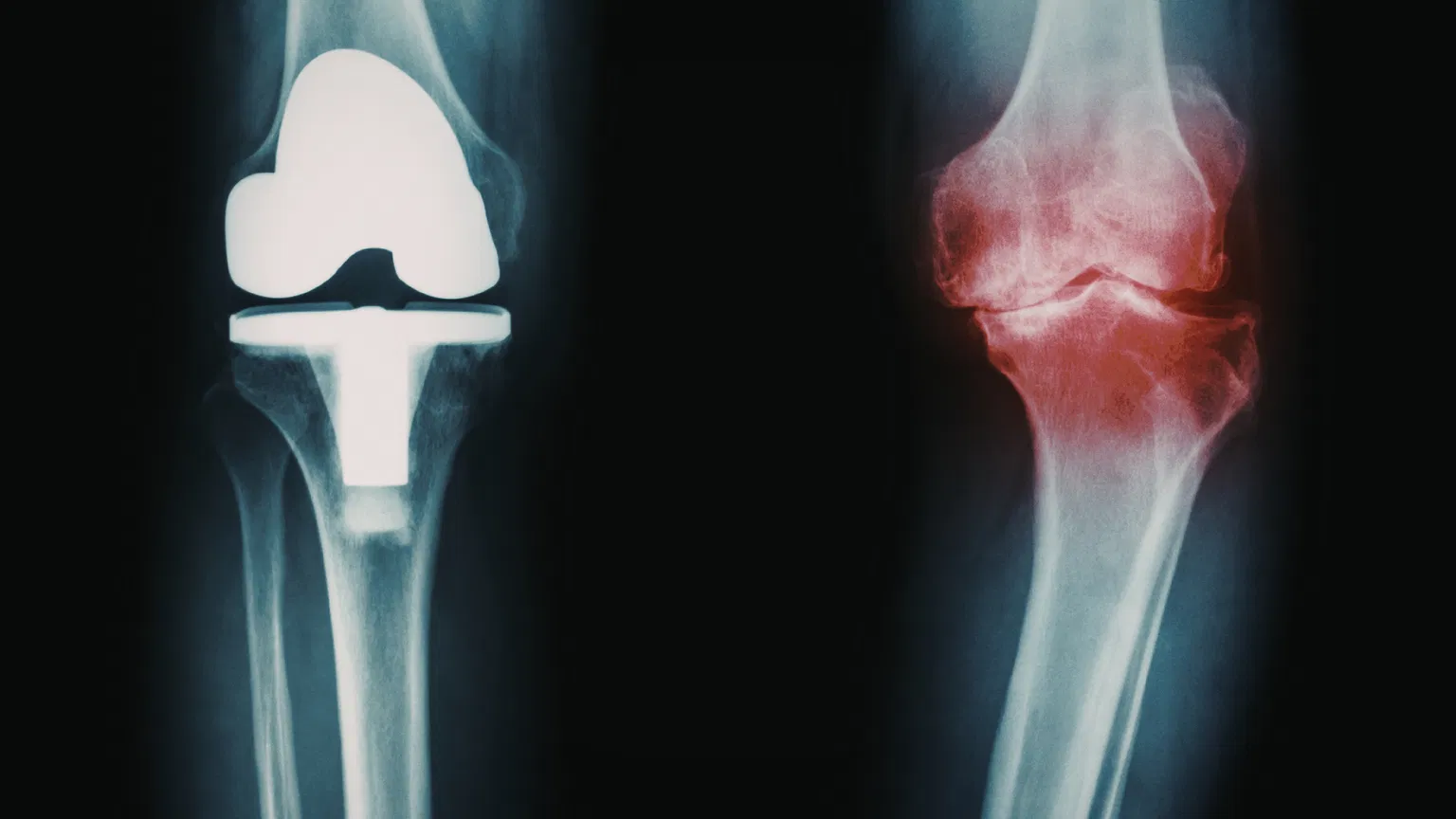
Key Characteristics of Partial Knee Replacement
-
Only one compartment of the knee is replaced
-
Smaller incision compared to total knee replacement
-
More natural knee movement after surgery
-
Faster recovery in selected patients
-
Less blood loss and tissue disruption
Because much of the original knee structure is preserved, partial knee replacement can feel more “natural” to some patients.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement is suitable only for carefully selected patients. You may be considered a candidate if:
-
Arthritis is limited to one compartment of the knee
-
Knee ligaments are strong and stable
-
Knee movement is reasonably good
-
Pain is mainly on one side of the knee
-
There is minimal or no knee deformity
It is important to understand that not everyone with knee pain is suitable for partial knee replacement. Proper evaluation by an experienced orthopedic surgeon is essential.
What Is Total Knee Replacement?
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a procedure in which all damaged surfaces of the knee joint are replaced with artificial implants. It is one of the most common and successful orthopedic surgeries worldwide.
Key Characteristics of Total Knee Replacement
-
All three compartments of the knee are resurfaced
-
Suitable for advanced and widespread arthritis
-
Corrects knee deformities such as bow legs or knock knees
-
Provides consistent and long-lasting pain relief
-
Improves stability and walking ability
Total knee replacement is often the best option when knee damage is extensive.
Who Needs Total Knee Replacement?
Total knee replacement is usually recommended when:
-
Arthritis affects more than one compartment
-
Knee pain is severe and constant
-
Stiffness significantly limits movement
-
Walking distance is very limited
-
The shape of the knee has changed due to deformity
-
Non-surgical treatments have failed
For patients with advanced arthritis, total knee replacement offers predictable and durable results.
Partial vs Total Knee Replacement: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between partial and total knee replacement helps clarify which procedure is more suitable.
Area of Knee Replaced
-
Partial Knee Replacement: Only the damaged compartment
-
Total Knee Replacement: Entire knee joint
Surgical Extent
-
Partial knee replacement is less extensive
-
Total knee replacement is more comprehensive
Recovery Time
-
Partial knee replacement generally allows quicker recovery
-
Total knee replacement requires longer rehabilitation
Pain Relief
-
Partial knee replacement works well for localized arthritis
-
Total knee replacement provides reliable pain relief for advanced arthritis
Implant Longevity
-
Partial knee replacement can last many years in selected patients
-
Total knee replacement typically lasts 15–20 years or more
How Doctors Decide Between Partial and Total Knee Replacement
Choosing the right type of knee replacement is a medical decision based on multiple factors.
Extent of Arthritis
X-rays and clinical examination help determine whether arthritis is limited to one compartment or spread throughout the knee.
Pain Severity
Constant pain that affects sleep and daily activities often points toward total knee replacement.
Knee Alignment and Stability
Significant deformity or ligament instability usually requires total knee replacement.
Age and Activity Level
-
Younger, active patients with localized arthritis may benefit from partial replacement
-
Older patients with widespread damage often need total replacement
Lifestyle and Expectations
The choice also depends on how much knee function is required for daily life and work.
Recovery After Partial Knee Replacement
Recovery after partial knee replacement is usually faster compared to total knee replacement.
What to Expect
-
Shorter hospital stay
-
Less post-operative pain
-
Early walking with support
-
Faster return to routine activities
-
Physiotherapy is still required, but for a shorter duration
Many patients resume daily activities within a few weeks, depending on overall health and commitment to rehabilitation.
Recovery After Total Knee Replacement
Recovery after total knee replacement is gradual and structured.
What to Expect
-
Hospital stay of a few days
-
Walking with support within days
-
Regular physiotherapy sessions
-
Gradual improvement in strength and flexibility
-
Full recovery may take several months
Although recovery takes longer, total knee replacement provides reliable long-term relief for severe knee arthritis.
Advantages and Limitations of Partial Knee Replacement
Advantages
-
Preserves healthy parts of the knee
-
Faster recovery
-
More natural knee feel
-
Smaller surgical incision
Limitations
-
Not suitable for all patients
-
Arthritis may progress in other compartments
-
May require conversion to total knee replacement in the future
Advantages and Limitations of Total Knee Replacement
Advantages
-
Treats advanced arthritis completely
-
Corrects deformities
-
Long-lasting pain relief
-
Suitable for most severe knee conditions
Limitations
-
Longer recovery period
-
More extensive surgery
-
Requires dedicated rehabilitation
Long-Term Results and Implant Life
Modern knee replacement implants are designed to last many years.
-
Partial knee replacements can last long when patient selection is correct
-
Total knee replacements often last 15–20 years or more
-
Implant life depends on weight, activity level, and overall joint care
Regular follow-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle help improve long-term outcomes.
When Should You See an Orthopedic Surgeon?
You should consult an orthopedic specialist if:
-
Knee pain persists for several months
-
Pain affects walking, sitting, or sleeping
-
Knee stiffness limits movement
-
Knee shape appears altered
-
Conservative treatments no longer work
Early evaluation helps prevent unnecessary delay and worsening of joint damage.
Choosing the Right Knee Replacement Specialist in Delhi
The success of knee replacement surgery depends on:
-
Accurate diagnosis
-
Proper procedure selection
-
Surgical expertise
-
Post-operative care and rehabilitation
The Joint Clinic – Dr. (Prof) Amite Pankaj Aggarwal, located in Rohini, Delhi, provides comprehensive evaluation and treatment for knee arthritis and joint replacement conditions. With a patient-focused approach, treatment decisions are based on clinical need, long-term outcomes, and individual lifestyle requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is partial knee replacement better than total knee replacement?
Partial knee replacement is better only for patients with arthritis limited to one compartment. Total knee replacement is more suitable for widespread knee damage.
Which knee replacement has a faster recovery?
Partial knee replacement generally has a faster recovery than total knee replacement.
Can a partial knee replacement be converted to a total knee replacement later?
Yes, if arthritis progresses to other compartments, partial knee replacement may need conversion to total knee replacement.
How long does knee replacement surgery last?
Most modern knee replacements last 15–20 years or longer with proper care.
How do I know which knee replacement is right for me?
An orthopedic surgeon evaluates X-rays, symptoms, knee stability, and lifestyle before recommending the most suitable option.
Conclusion
Deciding between partial and total knee replacement is an important step toward relieving chronic knee pain and restoring mobility. Each procedure has its own benefits and limitations, and the right choice depends on the extent of knee damage, the severity of pain, and individual needs.
If knee pain is limiting your daily life, a timely consultation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon can help you choose the most effective treatment and regain a comfortable, active lifestyle.

- Live Secret Key
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- Art
- Life
- Coding




